Laser etching leaves tracing by melting the surface of items and products. It falls within the more general category of laser marking, which also encompasses laser engraving and annealing. Laser etching is highly adaptable and works with the majority of metals. The laser beam concentrates a lot of energy into a small area to create a raised mark. The material’s surface melts and enlarges as a result. This can give the material a gray, white, or black hue. Permanent markings like data matrix codes, serial numbers, barcodes, and emblems are most frequently created by etching. Read More…
Great Lakes Engineering is a trend setting manufacturer of surface mount stencils, precision laser cut parts, and photo chemical etched parts. We work with a wide range of materials, including Stainless Steel, Copper, Brass, Titanium, Nitinol, Nickel, Kovar and many others.

Our teams at Remaly Manufacturing Company, Inc. utilize state of the art equipment to provide you with laser cutting capabilities. Our teams provide cutting services for a wide range of materials such as steel, aluminum, stainless steel, monel and much more.

Sharpe Products specializes in custom pipe and tube bending and tube laser cutting. With three powerful, 4kW laser cutting systems, and a robotic, multi-axis 3 kW laser cutting system, we cut round, square, rectangle and open profiles, up to 6-inch OD. Typical cutouts include angles, copes, notches, perforations, slots, or other custom hole patterns, either before or after tube bending. We work...

Our fiber optic metal laser cutting capabilities include Stainless steel, Aluminum, CRS and other ferrous and nonferrous metals. We can laser cut flat blanks, stencils, signs, prototypes, and custom formed fabricated parts.

At MET Manufacturing Group, we have built our reputation around delivering precision manufacturing solutions that empower our customers to bring complex projects to life. Our specialty lies in advanced laser cutting, where we combine state-of-the-art equipment with a highly skilled team to produce parts and components with unmatched accuracy.

More Laser Etching Companies

Laser Etching: Complete Guide to Process, Applications, Benefits, and Choosing Providers
Laser etching is a highly versatile marking and fabrication process used across a wide range of industries for both decorative and functional applications. Leveraging the precision and speed of fiber laser technology, laser etching offers a permanent way to mark, label, and personalize products made from materials such as glass, marble, stone, tile, wood, cardboard, aluminum, stainless steel, paper, cork, plastic, and polymers. This powerful technology is now a standard in industrial manufacturing, product identification, traceability, branding, and custom design. Whether you’re considering laser etching for industrial production, retail, art, or personalization, understanding the process, its benefits, and how to choose the right laser etching service provider can help you make an informed decision.
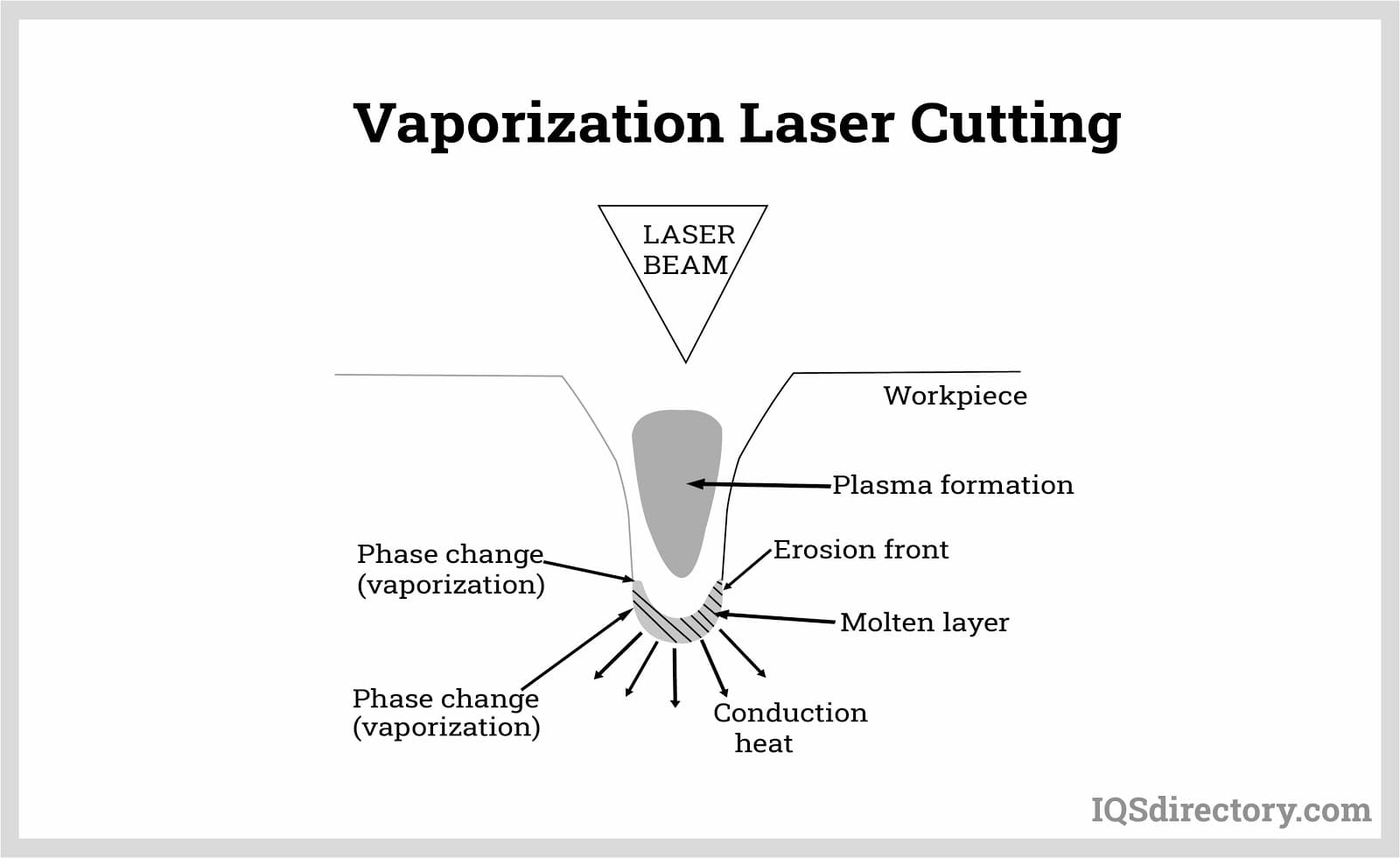
If you're researching the difference between laser etching and laser engraving, it's important to note that laser engraving removes material to produce deep, permanent lines or grooves, while laser etching melts the micro-surface to create slightly raised, high-contrast marks. Both methods use intense, focused heat to alter the surface of metals and other materials, leaving permanent and highly legible marks. While laser engraving is generally more robust and suited for deeper marking needs, laser etching is typically faster, making it the preferred method for high-throughput production and rapid prototyping where speed and clarity are critical.
How Does Laser Etching Work?
Laser etching is a computer-controlled process that uses a fiber laser machine to direct a concentrated beam of light at a specific wavelength onto the surface of a material. The controlled application of laser energy rapidly heats and melts the material’s surface, creating a high-contrast, permanent mark without significant material removal. This process is ideal for marking intricate designs, serial numbers, barcodes, logos, and other identifiers that require both durability and precision.
All laser marking techniques—including etching, engraving, and annealing—utilize pulsing, where the laser delivers quick, high-energy bursts at precisely timed intervals. Each pulse can deliver up to 10,000 watts of peak power, with pulse frequencies reaching up to 100,000 pulses per second. This allows for rapid marking with minimal thermal distortion, which is especially important for delicate or heat-sensitive materials.
When evaluating laser etching vs. laser engraving, a key distinction is the energy density and pulse separation: laser etching typically uses less energy per area and longer intervals between pulses, resulting in shallow, raised marks. Engraving, on the other hand, uses higher energy and more concentrated pulses to ablate material and create deeper grooves. This difference directly impacts both the visual effect and the suitability for various applications. For example, laser etching is perfect for parts that require readable, durable marks but cannot tolerate deep engraving.

Types of Laser Etching Machines
Choosing the right type of laser etching equipment is critical for achieving optimal results for your specific material, application, and production volume. Below are the primary types of laser etching machines and their typical uses:
Cylindrical Laser Etching Machine
Etching cylindrical objects—such as tumblers, mugs, pipes, cups, or wine glasses—presents unique challenges due to the need for 360° rotational marking. Cylindrical laser etching machines are engineered to precisely rotate the workpiece during processing, ensuring even, continuous marks around the circumference. These systems traverse a fine helical path, synchronizing movement and laser pulsing to generate high-resolution raster images, text, or graphics. This setup is essential for industries requiring branding, identification, or decorative marking on round products, such as drinkware manufacturers, automotive suppliers, and custom gift shops.

Fixed Laser Etching Machines
Fixed or stationary laser etching machines use stable work tables where both the laser source and the workpiece remain in place. Directional galvanometer (galvo) mirrors rapidly steer the laser beam across the target area, enabling high-speed, precise marking of both two-dimensional (vector) and image-based (raster) designs. This configuration is ideal for marking flat components, identification plates, electronic enclosures, or sheet goods—especially where high throughput and repeatability are required.
X-Y Type Laser Etching Machines
The X-Y type laser etching machine is the most prevalent and versatile option in the market. These systems either move the laser head along two axes (X-Y) over a stationary workpiece or manipulate the workpiece itself beneath a stationary laser. In certain configurations, the X-axis is assigned to the workpiece and the Y-axis to the laser (or vice versa). This flexible approach enables precise, detailed marking on both small and large flat surfaces, making it suitable for everything from electronics and jewelry to industrial part marking and signage.

Common Applications of Laser Etching
Laser etching technology is renowned for its versatility and is extensively used across multiple industries. Below are some of the most popular and high-value applications:
- Industrial part marking and traceability: Laser etching is ideal for permanent labeling of metal parts, such as serial numbers, barcodes, and QR codes, ensuring critical product traceability throughout the supply chain. Manufacturers in the automotive, aerospace, electronics, and medical device sectors rely on laser etching to comply with regulatory requirements and prevent counterfeiting.
- Product branding and customization: Companies use laser etching for adding logos, brand names, and custom graphics to products, boosting brand identity and supporting anti-tampering measures. This is particularly valuable for promotional items, awards, and corporate gifts.
- Marking heat-treated or coated components: Laser etching can mark heat-treated or powder-coated parts quickly and effectively. Raised marks produced by etching retain visibility and traceability even after post-processing treatments like e-coating or painting.
- High-speed production marking: The rapid processing speed of laser etching makes it the preferred solution for mass production environments where throughput, accuracy, and durability are essential.
- Art, design, and personalization: Artists and designers use laser etching to produce intricate artwork, patterns, and personalized engravings on a wide array of materials, including glass, wood, acrylic, and stone. The process enables high-resolution, repeatable designs that stand out visually.
- Medical instruments and devices: Due to its ability to produce sterile, corrosion-resistant, and durable marks, laser etching is widely used for labeling surgical tools, implants, and medical equipment. The non-contact nature of the process ensures no compromise to the integrity of sensitive components.
- Electronics and PCB marking: Laser etching is used to mark components and circuit boards with identification codes, component values, or branding, supporting automated assembly and quality control processes.
Key Benefits of Laser Etching for Manufacturers and Designers
Laser etching offers multiple competitive advantages that make it a compelling choice for manufacturers, fabricators, artists, and engineers. Key benefits include:
- Extensive material compatibility: Laser etching can be used on a broad range of materials, including metals (stainless steel, aluminum, titanium, brass), plastics, ceramics, glass, leather, wood, acrylic, and composites. This makes it suitable for diverse industries and product types.
- Adaptability to part thickness: Whether you need to etch thin foils or thick blocks, the process can be tuned for optimal results, making it ideal for everything from delicate jewelry to heavy machine components.
- High precision and detail: The focused laser beam allows for extremely fine lines, intricate designs, micro-text, and data matrices—perfect for applications demanding high legibility and accuracy, such as electronics and medical devices.
- Non-contact, low-stress process: Laser etching is a non-contact method, meaning it does not physically touch or deform the material. This reduces the risk of contamination, mechanical stress, or damage, which is especially important for sensitive or high-value parts.
- Cost-effective and energy efficient: Modern laser etching systems are highly energy-efficient and require minimal consumables, resulting in lower operating costs, less maintenance, and greater environmental sustainability compared to traditional marking methods (e.g., stamping, chemical etching).
- Fast turnaround and scalability: Laser etching is optimized for rapid processing, supporting high-volume production and just-in-time manufacturing. Its speed and precision mean it can meet tight deadlines and respond to changing production needs quickly.
- Permanent, tamper-proof marks: Unlike ink or stickers, laser-etched marks are permanent and cannot be easily removed, faded, or altered. This improves product security, supports regulatory compliance, and enhances consumer trust.
Laser Etching vs. Other Marking Methods
When deciding how to mark or personalize products, it’s helpful to compare laser etching to alternative techniques such as mechanical engraving, chemical etching, pad printing, inkjet marking, and stamping. Here’s how laser etching stands out:
- Precision and quality: Laser etching produces cleaner, more consistent marks than mechanical or chemical methods, with less risk of material deformation or hazardous waste.
- Versatility: Unlike pad printing or inkjet, laser etching works on metals, plastics, glass, ceramics, and more, offering flexibility for manufacturers who work with varied product lines.
- Environmental safety: Laser etching is a dry, clean process that doesn’t require solvents, acids, or other hazardous chemicals. This reduces waste and ensures a safer work environment.
- Low maintenance and automation: Laser etching machines are highly reliable, easy to automate, and require minimal intervention, making them ideal for modern smart manufacturing facilities.
Industries That Rely on Laser Etching
Laser etching technology is trusted by a wide variety of industries where permanent, high-precision marks are essential. Some of the leading sectors include:
- Automotive manufacturing: VIN numbers, component branding, and traceability for critical parts.
- Aerospace and defense: Marking of serial numbers, part numbers, and safety information on high-value components.
- Medical and dental devices: Marking of surgical tools, implants, and instruments to ensure traceability and compliance with FDA and MDR regulations.
- Consumer electronics: Branding, product codes, and regulatory labels on gadgets, devices, and circuit boards.
- Jewelry and luxury goods: Custom engraving, serial numbers, and anti-counterfeiting marks on watches, rings, and collectibles.
- Industrial equipment and tooling: Identification, calibration marks, and safety labels on machine parts and hand tools.
- Promotional products and awards: Personalization of trophies, plaques, and branded merchandise.
How to Choose the Right Laser Etching Company
Selecting a reliable and experienced laser etching service provider is crucial for achieving the quality, speed, and value your project requires. Here are some key factors and decision criteria to consider when evaluating laser etching companies:
- Technical expertise and experience: Look for providers with a proven track record in your material type and application (e.g., metals, plastics, complex geometries). Experience with your industry’s standards (such as ISO, FDA, or automotive requirements) is a major plus.
- Equipment capabilities: Ensure the company uses modern, well-maintained fiber laser systems that can handle your part size, shape, and production volume.
- Customization and design support: Does the provider offer in-house design services, prototyping, or help with optimizing artwork for laser etching? This can accelerate your development cycle.
- Quality assurance and traceability: Ask about their inspection processes, documentation, and ability to provide test samples or certifications.
- Turnaround time and scalability: Can they meet your timeline for both prototypes and full-scale production? Do they offer expedited services or flexible scheduling?
- Cost transparency: Request quotes and compare pricing, but also consider value-added services such as logistics, packaging, or post-processing.
- Customer reviews and references: Research customer feedback and ask for case studies or references to validate their claims.
To streamline your selection process, use our comprehensive directory of laser etching businesses. Each company profile highlights their specialties, capabilities, and certifications, and includes a direct contact form for inquiries or quote requests. You can preview each provider’s website using our patented website previewer before making a decision, and submit a single Request for Quote (RFQ) form to contact multiple companies simultaneously. Ready to compare laser etching providers? Click here to get started!
Frequently Asked Questions About Laser Etching
- What materials can be laser etched? Most metals (steel, aluminum, brass, titanium), plastics, ceramics, glass, leather, wood, and composites can be etched. Some specialized materials may require testing for optimal results.
- Is laser etching permanent? Yes, laser-etched marks are highly durable, resistant to abrasion, chemicals, and fading, making them suitable for industrial, medical, and consumer goods.
- How does laser etching compare to laser engraving? Laser etching melts the surface to create raised marks, while engraving removes material for deeper grooves. Etching is faster; engraving is more robust for deep or harsh-environment applications.
- What is the typical lead time for laser etching projects? Lead times vary based on project complexity and volume, but many providers offer rapid turnaround, especially for standard material types and designs.
- Can I supply my own artwork or CAD files? Most laser etching companies accept customer-supplied artwork, drawings, or CAD files. Some offer design assistance to optimize files for best results.
- Is laser etching safe and environmentally friendly? Yes, laser etching is a clean, non-contact process that does not use hazardous chemicals, making it safe for workers and the environment.
- What industries benefit most from laser etching? Automotive, aerospace, medical, electronics, jewelry, consumer goods, and manufacturing sectors all leverage laser etching for traceability, branding, and compliance.
Get Started: Next Steps for Laser Etching Projects
Are you ready to take the next step with laser etching? Whether you need part marking, product branding, custom artwork, or high-volume production, our network of vetted laser etching companies can provide quotes, technical advice, and design support. Contact us today to discuss your project, compare service providers, or request samples. For more information on related processes, explore our in-depth guides on laser engraving.
Still Have Questions?
Looking for a fast quote on your laser etching project? Want to compare machine types or material compatibility? Need help deciding between laser etching and engraving for your application? Ask our experts or request a consultation now! Explore our FAQ section above or browse our knowledge base for detailed answers to common questions about laser etching, marking, and related manufacturing processes.








 Broaching
Broaching CNC Machining
CNC Machining Expanded Metals
Expanded Metals Laser Cutting
Laser Cutting Metal Etching
Metal Etching Metal Fabrication
Metal Fabrication Perforated Metals
Perforated Metals Screw Machine Products
Screw Machine Products Metal Stampings
Metal Stampings Sheet Metal Fabrication
Sheet Metal Fabrication Tube Fabrication
Tube Fabrication Water Jet Cutting
Water Jet Cutting Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services